
Name of the rose
Dr Nabil Elmahdawi on gynaecological rejuvenation in menopausal women and the Nrose protocol
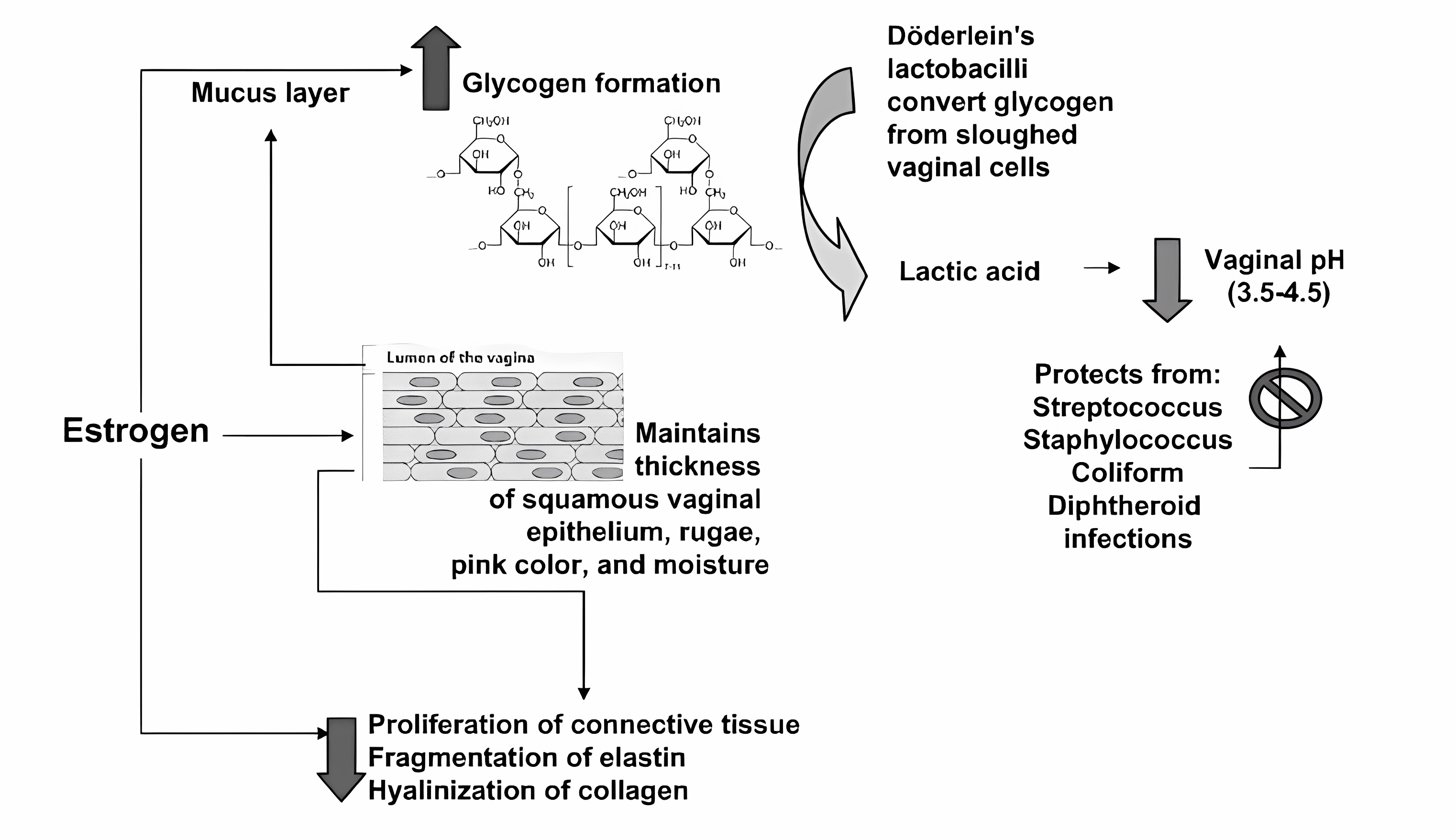
Menopause brings about significant changes in urogenital health for women. Urogenital atrophy is a physiological condition which most often occurs during and after menopause when the lack of the female hormone oestrogen affects the vagina, urethra and bladder trigone. After the menopause, the amount of oestrogen produced by the ovaries falls.
The lack of oestrogen leads to a thinning of the tissues around the vaginal area and a reduction in the number of small mucus-producing glands. There is also a loss of fat around the genitals, producing a different appearance than previously.
As a result, the vagina is shortened and loses elasticity with less lubricating mucus; the genital skin also looks paler. These changes usually take months or years and vary between women.
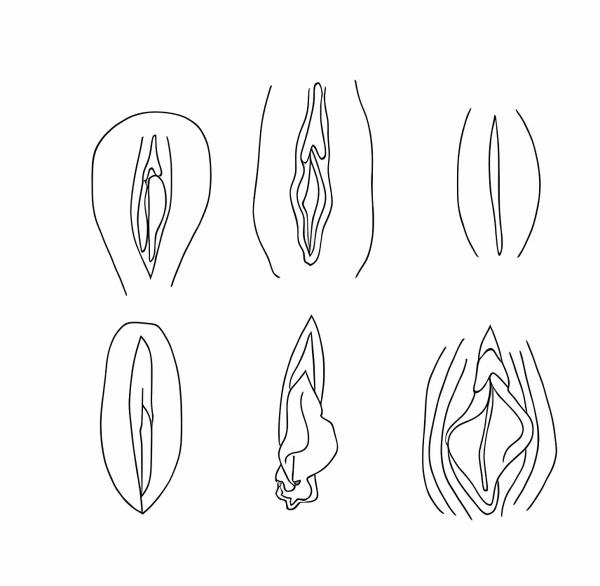
With age, at puberty, the labia become gradually larger and thicker, but the chief difference is in the keratinisation, which changes at a cellular level.
After puberty, the labia become more easily visible as their prominence increases.
As a woman continues to grow more mature, there is also an increase in labial thickness and length after pregnancy and delivery.

Menopause
- Dryness (estimated 75%)
- Dyspareunia (estimated 38%)
- Vaginal itching, discharge, and pain (estimated 15%)
- Urinary symptoms associated with vaginal atrophy:
- Dysuria, nocturia, and urgency
- Urinary incontinence
- Recurrent urinary tract infections
Other medical conditions can result in early menopause, like cancer and cancer treatment with anti-cancer systemic therapy and radiation and other familial conditions. This is predominantly due to the lack of oestrogen production after that resulted in the change and lack of proliferation of the vaginal epithelium.
Caption: Schematic depiction of the effects of oestrogen on the vaginal epithelium2
Unfortunately, most women suffer in silence. In the VIVA study, nearly half (47%) of women who eventually saw an HCP about their symptoms waited more than six months, whereas 28% waited more than one year and 15% waited more than two years.1,3
According to the North American Menopause Society, up to 85% of menopausal women may experience urogenital dysfunction symptoms, and approximately 50% of postmenopausal women have these symptoms that impact urosexual function and quality of life, however, up to 1/3 of patients or more will never seek any medical help.
Common procedures in managing urogenital changes:
- Vaginal lubricants and moisturisers: Over-the-counter vaginal lubricants and moisturisers can help alleviate vaginal dryness and discomfort during sexual activity.
- Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT): For women experiencing severe symptoms, hormone replacement therapy may be considered to supplement declining oestrogen levels and alleviate urogenital issues. However, HRT is not suitable for everyone, and its risks and benefits should be discussed with a healthcare professional.
- Pelvic floor exercises: Strengthening pelvic floor muscles through Kegel exercises may help improve bladder control.
- Topical oestrogen therapy: For some women, localised oestrogen treatments in the form of creams, rings, or tablets may be prescribed to address vaginal atrophy without systemic effects.
- Behavioural strategies for urinary incontinence: Lifestyle modifications, bladder training, and avoiding certain triggers can help manage urinary incontinence.
- Maintaining good hygiene: Proper hygiene practices can reduce the risk of urinary tract infections.
Other new emerging techniques to help vaginal rejuvenation rely on the use of non-hormonal based therapies like hyaluronic acid, Platelet Rich Plasma (PRP), growth factor serums and energy devices like radiofrequency and laser.
The Nrose® Protocol
The Nrose® protocol is the first non-hormonal combination therapy that has resulted in proven evidence of restoration of the urogenital physiology and alleviation of symptoms.
Nrose® protocol is made up of three important steps:
- Labia majora physiological volume restoration using Intense Rose hyaluronic acid injectable gel.
- Bipolar fractionated radiofrequency to restore and promote vaginal mucosa and vulval skin restoration.
- The continuous use of the rejuvenation Rose gel intimal non-hormonal care serum to maintain and improve intimal health.
The Nrose® protocol has shown, according to Piotr Kolczewski, HA and radiofrequency for a holistic approach to the intimate area rejuvenation, 100% of patients satisfied with the volumetric effect after treatment, 100% improvement of the appearance of the vulva after the treatment, 100% of patients reported an increase in the vaginal hydration and 75% improvement in the urinary incontinence.4
Step 1: Labia volume restoration
This is done by Intense Rose gel, which is a hyaluronic acid 28mg/ml PEG polymer cross-linked gel. It comes in a 1ml syringe mixed with glycine and L-Proline to increase the level of the osmotic balance. Proline and glycine are crucial for stabilising the structure of the hydrogel, especially in terms of viscoelastic properties and thermodynamic balance. It is the only HA filler indicted and licenced for vulva atrophy correction and related symptoms.
P. Kubik, W. Gruszczynskiet et al. published in the Academy of Aesthetic and Anit-Aging Medicine in Dermatologic Therapy that the advantage of Intense Rose gel on any other HA fillers due to PEG cross-linking is thermostability important not only from the pure resistance perspective.5 Results of the study point to the conclusion that the heat resistance of HA fillers cross-linking agent depends selection of dermal fillers is crucial in this case of using IR, RF, HIFU (or any other heat emitting device) over the injected filler and exposure of human PMN to Neauvia filler results in reduced migration and oxidative metabolism, as well as in reduced mRNA levels of key proinflammatory mediators like TNF-α and IL-8.
The outcome of augmentation and restoration of the Labia Majora Intense Rose Hydrogel HA -PEG Polymer, as published in the Journal of Biological Regulators and Homeostatic Agents by Zerbinati et al., was astonishing.6 Almost 100 % of patients (97-100) out of 37 patients in the trial with labia hypotrophy, with an average age of 45 years old (36-68), tested for elasticity, volume, and overall evaluation of appearance have shown a significant and mean full improvement in all tested parameters.
The procedure of volume restoration in the aesthetic industry is called labia puff. It is performed using dermal fillers in a non-surgical treatment procedure and takes approximately 20 to 30 minutes. Using an aseptic technique, the medical practitioner will first inject a local anaesthetic into the labia before injecting a precise amount of filler into the labia majora for volume enhancement as per the diagram. The treatment results can be seen immediately, and patients can return to their normal activities as soon as the procedure is completed. Dermal fillers used for labia puffing in our clinic last for approximately nine to 12 months and will require top-up injections to maintain the results.
The average amount in ml of Intense Rose Gel is 4ml (range 2 -6), which, in my experience, is sufficient.
